MS Azure: 7 Powerful Reasons to Choose This Ultimate Cloud Platform
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses operate, and MS Azure stands at the forefront of this revolution. With unmatched scalability, global reach, and enterprise-grade security, it’s no wonder millions trust Microsoft’s cloud ecosystem for their digital transformation.
What Is MS Azure and Why It Matters

Microsoft Azure, commonly referred to as MS Azure, is a comprehensive cloud computing platform developed by Microsoft. Launched in 2010, it offers over 200 services ranging from virtual machines and databases to AI and IoT solutions. Unlike traditional on-premise infrastructure, MS Azure enables organizations to scale resources dynamically, reduce capital expenditure, and innovate faster.
Origins and Evolution of MS Azure
MS Azure began as Windows Azure in 2010, primarily offering platform-as-a-service (PaaS) capabilities. Over the years, it evolved into a full-fledged infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) and software-as-a-service (SaaS) provider. By 2014, Microsoft rebranded it to Microsoft Azure to reflect its broader capabilities beyond Windows-based applications.
- 2010: Launch as Windows Azure with basic PaaS features
- 2014: Rebranding to Microsoft Azure, expansion into IaaS
- 2018–2023: Rapid growth in AI, hybrid cloud, and edge computing
This evolution mirrors the industry’s shift toward hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Today, MS Azure powers everything from small startups to Fortune 500 companies, including BMW, Adobe, and Walmart.
Core Components of MS Azure
MS Azure is built around several foundational components that enable diverse workloads. These include compute, storage, networking, and management tools. Each component integrates seamlessly, allowing developers and IT professionals to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently.
- Compute: Virtual Machines, Azure App Services, Functions, and Kubernetes (AKS)
- Storage: Blob Storage, Disk Storage, Data Lake, and Archive Storage
- Networking: Virtual Networks, Load Balancer, DNS, and Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Management: Azure Monitor, Resource Manager, and Automation
These services are accessible via the Azure portal, command-line interface (CLI), PowerShell, or APIs, giving users flexibility in how they interact with the platform.
“Azure is not just a cloud platform; it’s a complete digital transformation engine.” — Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
MS Azure vs. Competitors: A Strategic Advantage
In the competitive landscape of cloud providers, MS Azure competes directly with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). While AWS leads in market share, MS Azure differentiates itself through deep integration with Microsoft products, hybrid cloud capabilities, and strong enterprise support.
Market Position and Global Reach
According to Synergy Research Group (2023), MS Azure holds approximately 23% of the global cloud infrastructure market, second only to AWS. Its presence spans 60+ regions worldwide, more than any other cloud provider, ensuring low-latency access and compliance with local data regulations.
- Regions in North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Africa, and South America
- Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and other global standards
- Support for sovereign clouds like Azure Government and Azure Germany
This global footprint makes MS Azure ideal for multinational corporations requiring data residency and regulatory compliance.
Integration with Microsoft Ecosystem
One of MS Azure’s biggest strengths is its seamless integration with Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, Active Directory, and Power Platform. Organizations already using Microsoft tools can extend their capabilities into the cloud without major retraining or system overhauls.
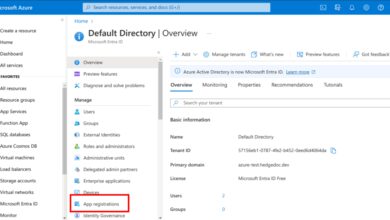
- Single sign-on (SSO) via Azure Active Directory
- Automated workflows using Power Automate
- AI-powered analytics with Power BI and Azure Synapse
This synergy reduces friction during migration and accelerates time-to-value for new cloud initiatives.
Key Services Offered by MS Azure
MS Azure provides a vast array of services across multiple domains. Understanding these services helps businesses choose the right tools for their needs, whether it’s hosting web applications, analyzing big data, or deploying machine learning models.
Compute and Virtualization
MS Azure offers flexible compute options tailored to various performance and cost requirements. From scalable virtual machines to serverless computing, Azure ensures optimal resource utilization.
- Azure Virtual Machines: Run Windows or Linux VMs with customizable CPU, memory, and storage
- Azure App Service: Host web apps without managing infrastructure
- Azure Functions: Execute code in response to events (serverless)
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Manage containerized applications at scale
For example, a retail company can use Azure App Service to host its e-commerce site and scale automatically during holiday traffic spikes.
Data and Analytics Solutions
Data is the lifeblood of modern enterprises, and MS Azure provides robust tools for storing, processing, and analyzing it. Whether dealing with structured databases or unstructured data lakes, Azure has a solution.
- Azure SQL Database: Fully managed relational database service
- Azure Cosmos DB: Globally distributed NoSQL database for high availability
- Azure Synapse Analytics: Unified analytics platform for big data and data warehousing
- Azure Data Factory: Orchestrate data pipelines across on-premises and cloud sources
Companies like Coca-Cola use Azure Synapse to analyze customer behavior and optimize supply chains in real time.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
MS Azure is a leader in democratizing AI. Its Cognitive Services, Bot Framework, and Azure Machine Learning allow developers to build intelligent applications without deep expertise in data science.
- Azure Cognitive Services: Pre-built APIs for vision, speech, language, and decision-making
- Azure Machine Learning: End-to-end platform for training, deploying, and monitoring ML models
- Azure OpenAI Service: Access to advanced models like GPT-4 for natural language processing
For instance, healthcare providers use Azure AI to analyze medical images and detect anomalies faster than human radiologists.
Security and Compliance in MS Azure
Security is a top concern for any organization moving to the cloud. MS Azure addresses this with a multi-layered approach that includes physical security, network protection, identity management, and compliance certifications.
Built-In Security Features
MS Azure provides a suite of security tools designed to protect data and applications. These tools are integrated into the platform, reducing the complexity of securing cloud environments.
- Azure Security Center: Unified security management and threat protection
- Azure Defender: Advanced threat detection for servers, storage, and SQL databases
- Azure Firewall: Managed, cloud-native firewall service
- DDoS Protection: Mitigates distributed denial-of-service attacks
These services continuously monitor for suspicious activity and provide automated responses to potential threats.
Identity and Access Management
Controlling who can access what resources is critical in cloud environments. MS Azure uses Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) as its identity and access management backbone.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced login security
- Conditional access policies based on user location, device, or risk level
- Role-based access control (RBAC) for granular permissions
Organizations can enforce zero-trust security models, ensuring users are verified every time they access sensitive data.
“Security is not a product, but a process. Azure embeds it at every layer.” — Microsoft Trust Center
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Capabilities of MS Azure
Not all businesses can move entirely to the cloud. Many require hybrid solutions that connect on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources. MS Azure excels in this area with services designed for seamless integration between environments.
Azure Arc: Bridging On-Premises and Cloud
Azure Arc extends Azure’s management capabilities to servers, Kubernetes clusters, and data services running anywhere—on-premises, at the edge, or in other clouds.
- Manage non-Azure resources using Azure Resource Manager
- Apply consistent policies and governance across environments
- Deploy Azure services like SQL Managed Instance outside Azure datacenters
This allows IT teams to use a single control plane for all their infrastructure, regardless of location.
Azure Stack: Bringing the Cloud On-Premises
Azure Stack is a family of products that delivers Azure services in on-premises datacenters. It includes Azure Stack Hub, Edge, and HCI, catering to different deployment needs.
- Azure Stack Hub: Full Azure services in your datacenter for regulated industries
- Azure Stack Edge: AI-enabled edge devices with local processing and cloud connectivity
- Azure Stack HCI: Hyperconverged infrastructure for virtualized workloads
Industries like defense and healthcare use Azure Stack to meet strict data sovereignty requirements while benefiting from cloud innovation.
Cost Management and Pricing Models in MS Azure
Understanding how MS Azure is priced is crucial for budgeting and optimizing cloud spending. Unlike traditional IT costs, cloud pricing is usage-based, which offers flexibility but requires careful monitoring.
Pricing Tiers and Models
MS Azure offers several pricing models to suit different usage patterns:
- Pay-as-you-go: Pay only for what you use, ideal for variable workloads
- Reserved Instances: Commit to 1- or 3-year terms for up to 72% savings on VMs
- Spot Instances: Use unused capacity at up to 90% discount for fault-tolerant workloads
- Hybrid Benefit: Save up to 40% by using existing Windows Server and SQL Server licenses
For example, a startup might start with pay-as-you-go and later purchase reserved instances as usage stabilizes.
Tools for Cost Optimization
MS Azure provides tools to help organizations track, analyze, and reduce their cloud costs.
- Azure Cost Management + Billing: Monitor spending, set budgets, and receive alerts
- Azure Advisor: Get personalized recommendations for cost savings and performance improvements
- Right-sizing Recommendations: Identify underutilized VMs and resize them for efficiency
These tools empower finance and IT teams to collaborate on cost-effective cloud strategies.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories with MS Azure
The true value of MS Azure is best illustrated through real-world implementations. Across industries, organizations leverage Azure to solve complex challenges and drive innovation.
Healthcare: Transforming Patient Care
Partners HealthCare uses MS Azure to process and analyze vast amounts of medical data. By leveraging Azure AI and machine learning, they’ve improved diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment plans.
- Reduced data processing time from days to minutes
- Enabled real-time monitoring of patient vitals using IoT devices
- Enhanced collaboration between hospitals using Azure-based telemedicine platforms
This has led to faster interventions and better patient outcomes.
Retail: Enhancing Customer Experience
Walmart uses MS Azure to power its e-commerce platform and supply chain logistics. With Azure’s scalability, Walmart handles millions of transactions during peak shopping seasons without downtime.
- Personalized recommendations using Azure Machine Learning
- Inventory optimization through real-time analytics
- Secure payment processing with Azure security tools
The result is a seamless shopping experience across online and physical stores.
Manufacturing: Driving Industry 4.0
BMW leverages MS Azure for predictive maintenance and smart factory operations. Sensors on production lines send data to Azure IoT Hub, where it’s analyzed to predict equipment failures before they occur.
- Reduced unplanned downtime by 30%
- Improved production efficiency through real-time monitoring
- Enabled remote diagnostics and software updates via Azure
This digital transformation has positioned BMW as a leader in smart manufacturing.
Getting Started with MS Azure: A Step-by-Step Guide
Starting with MS Azure can seem daunting, but Microsoft provides extensive resources to help new users. Whether you’re an individual developer or an enterprise team, there’s a clear path to adoption.
Creating an Azure Account
The first step is signing up for an Azure account. Microsoft offers a free tier with $200 in credits for 30 days and access to over 25 always-free services.
- Visit azure.microsoft.com and click “Start free”
- Provide basic information and a credit card (for verification only)
- Access the Azure portal and explore available services
No upfront cost is required, making it risk-free to experiment.
Learning Resources and Certification
Microsoft Learn is a free, interactive platform that offers learning paths for Azure fundamentals, administration, development, and architecture.
- Azure Fundamentals (AZ-900): Entry-level certification for beginners
- Azure Administrator (AZ-104): For managing Azure environments
- Azure Solutions Architect (AZ-305): For designing cloud solutions
These certifications are recognized globally and can boost career prospects in IT and cloud computing.
What is MS Azure used for?
MS Azure is used for a wide range of purposes, including hosting websites and applications, storing and analyzing data, running virtual machines, deploying AI models, and managing IoT devices. It supports both cloud-native and hybrid environments, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
How does MS Azure compare to AWS?
While AWS has a larger market share, MS Azure excels in integration with Microsoft products, hybrid cloud capabilities, and enterprise support. Azure is often preferred by organizations already using Microsoft 365, Active Directory, or .NET frameworks.
Is MS Azure secure?
Yes, MS Azure is highly secure, with built-in features like Azure Security Center, Azure Defender, and compliance with global standards such as GDPR and HIPAA. Microsoft invests over $1 billion annually in cybersecurity research and development.
Can I use MS Azure for free?
Yes, MS Azure offers a free account with $200 in credits for 30 days and access to many always-free services like Azure Functions, Blob Storage, and App Service. This allows users to learn and experiment without cost.
How do I get certified in MS Azure?
You can get certified through Microsoft Learn, which offers free training modules and practice exams. Popular certifications include AZ-900 (Azure Fundamentals), AZ-104 (Azure Administrator), and AZ-305 (Azure Solutions Architect). Exams are administered by Pearson VUE or Certiport.
MS Azure has firmly established itself as a leading cloud platform, offering a powerful blend of innovation, security, and integration. From startups to global enterprises, organizations leverage its vast array of services to drive digital transformation. Whether you’re looking to host applications, analyze data, or deploy AI, MS Azure provides the tools and infrastructure to succeed. With continuous updates, a global network, and strong support, it remains a top choice for businesses navigating the future of technology.
Further Reading: